Evidence of a drowned “microcontinent” has been found in sand grains from the beaches of a small Indian Ocean island, scientists say.
A well-known tourist destination, Mauritius (map) is located about 1,200 miles (2,000 kilometers) off the coast of Africa, east of Madagascar. Scientists think the tiny island formed some nine million years ago from cooling lava spewed by undersea volcanoes.
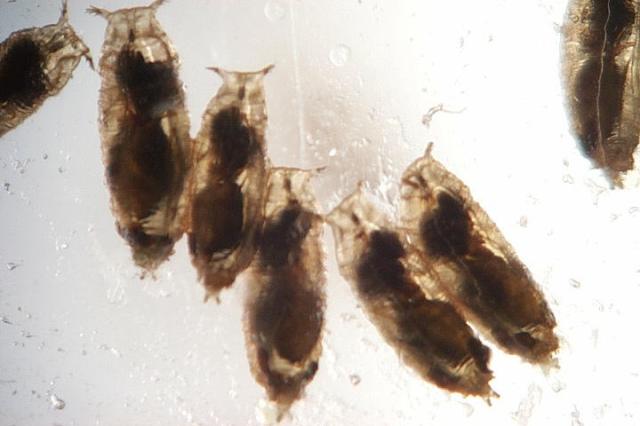
But recently, researchers have found sand grains on Mauritius that contain fragments of the mineral zircon that are far older than the island, between 660 million and about 2 billion years old.
In a new study, detailed in the current issue of the journal Nature Geoscience, scientists concluded that the older minerals once belonged to a now vanished landmass, tiny bits of which were dragged up to the surface during the formation of Mauritius.
“When lavas moved through continental material on the way towards the surface, they picked up a few rocks containing zircon,” study co-author Bjørn Jamtveit, a geologist at the University of Oslo in Norway, explained in an email.
Most of these rocks probably disintegrated and melted due to the high temperatures of the lavas, but some grains of zircons survived and were frozen into the lavas [during the eruption] and rolled down to form rocks on the Mauritian surface.”
Jamtveit and his colleagues estimate that the lost microcontinent, which they have dubbed Mauritia, was about a quarter of the size of Madagascar.
Furthermore, based on a recalculation of how the ancient continents drifted apart, the scientists concluded that Mauritia was once a tiny part of a much larger “supercontinent” that included India and Madagascar, called Rodinia.
The three landmasses “were tucked together in one big continent prior to the formation of the Indian Ocean,” Jamtveit said.
But like a prehistoric Atlantis, Mauritia was eventually drowned beneath the waves when India broke apart from Madagascar about 85 million years ago.
Scientists have long suspected that volcanic islands might contain evidence of lost continents, and Jamtveit and his team decided to test this hypothesis during a layover in Mauritius as part of a longer research trip in 1999.
The stop in tropical Mauritius “was a very tempting thing to do for a Norwegian in the cold month of January,” Jamtveit said.
Mauritius was a good test site because it was a relatively young island and, being formed from ocean lava, would not naturally contain zircon, a tough mineral that doesn’t weather easily.
If zircon older than nine million years was found on Mauritius, it would be good evidence of the presence of buried continental material, Jamtveit explained.
At first, the scientists crushed rocks from Mauritius to extract the zircon crystals, but this proved difficult because the crushing equipment contained zircon from other sites, raising the issue of contamination.
“That was a show stopper for a while,” Jamtveit said.
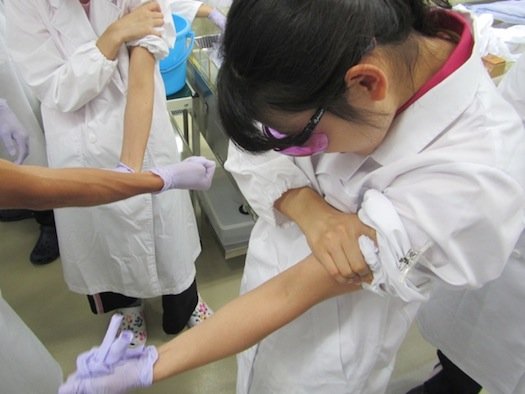
A few years later, however, some members of the team returned to Mauritius and this time brought back sand from two different beaches for sampling.
The scientists extracted 20 zircon samples and successfully dated 8 of them by calculating the rate that the elements uranium and thorium inside of the samples slowly break down into lead.
“They all provided much older ages than the age of the Mauritius lavas,” Jamtveit said. “In fact they gave ages consistent with the ages of known continental rocks in Madagascar, Seychelles, and India.”
Jérôme Dyment, a geologist at the Paris Institute of Earth Physics in France, said he’s unconvinced by the work because it’s possible that the ancient zircons found their way to the island by other means, for example as part of ship ballast or modern construction material.
“Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence, which are not given by the authors so far,” said Dyment, who did not participate in the research.
“Finding zircons in sand is one thing, finding them within a rock is another one … Finding the enclave of deep rocks that, according to the author’s inference, bring them to the surface during an eruption would be much more convincing evidence.”
Dyment added that if Mauritia was real, evidence for its existence should be found as part of a joint French and German experiment that installed deep-sea seismometers to investigate Earth’s mantle around Réunion Island, which is situated about 120 miles (200 kilometers) from Mauritius.
“If a microcontinent lies under Réunion, it should be depicted by this experiment,” said Dyment, who is part of the project, dubbed RHUM-RUM.
But Conall Mac Niocaill, a geologist at the University of Oxford in the U.K. who was also not involved in the study, said “the lines of evidence are, individually, only suggestive, but collectively they add up to a compelling story.”
The zircons “produce a range of ages, but all yield ages older than 660 million years, and one is almost 2 billion years old,” he added.
“There is no obvious source for them in Mauritius, and they are unlikely to have been blown in by the wind, or carried in by human activity, so the obvious conclusion is that the young volcanic lava sampled some older material on their way through the crust.”
Based on the new findings, Mac Niocaill and others think other vanished microcontinents could be lurking beneath the Indian Ocean.
In fact, analyses of Earth’s gravitational field have revealed other areas in the world’s oceans where the rock appears to be thicker than normal and could be a sign of continental crusts.
“We know more about the topography of Mars than we do about the [topography] of the world’s ocean floor, so there may well be other dismembered continents out there waiting to be discovered.”